What is this about?
What is a building energy model?
Building-related heat flows are well understood and models are extensively described by Hensen & Lamberts [2011], Underwood & Yik [2008] and Clarke [2000]. The figure below provides an overview of key energy flows that are considered in buildings. The figure shows a room that is influenced by its environment due to envelope transmission losses, infiltration, ventilation and solar gains. The indoor climate is, however, also influenced by multiple internal energy flows such as plug loads as well as emitted heat from occupants. These flows are not always in balance and hence heating, cooling and ventilation systems are required to provide a comfortable indoor environment.
Heat and mass transfer considered in a room: In order to accurately model these constantly changing and dynamically interacting flows, substantial research efforts have gone into the development of dynamic building-performance-simulation engines. The first generation of BPS engines emerged in the eighties and nineties to overcome limitations of the until then common steady-state single room heat balance models. The purpose of “dynamic” models using computational heat transfer methods such as response functions or finite-difference methods was to model transient thermal-mass effects [Clarke, 2000]. The BPS engines that is used by Archsim is EnergyPlus [Crawley et al., 2000]. EnergyPlus has been thoroughly validated and tested in practice so that whole buildings and their HVAC systems can be modeled reliably [ANSI/ASHRAE, 2011] and in great detail.
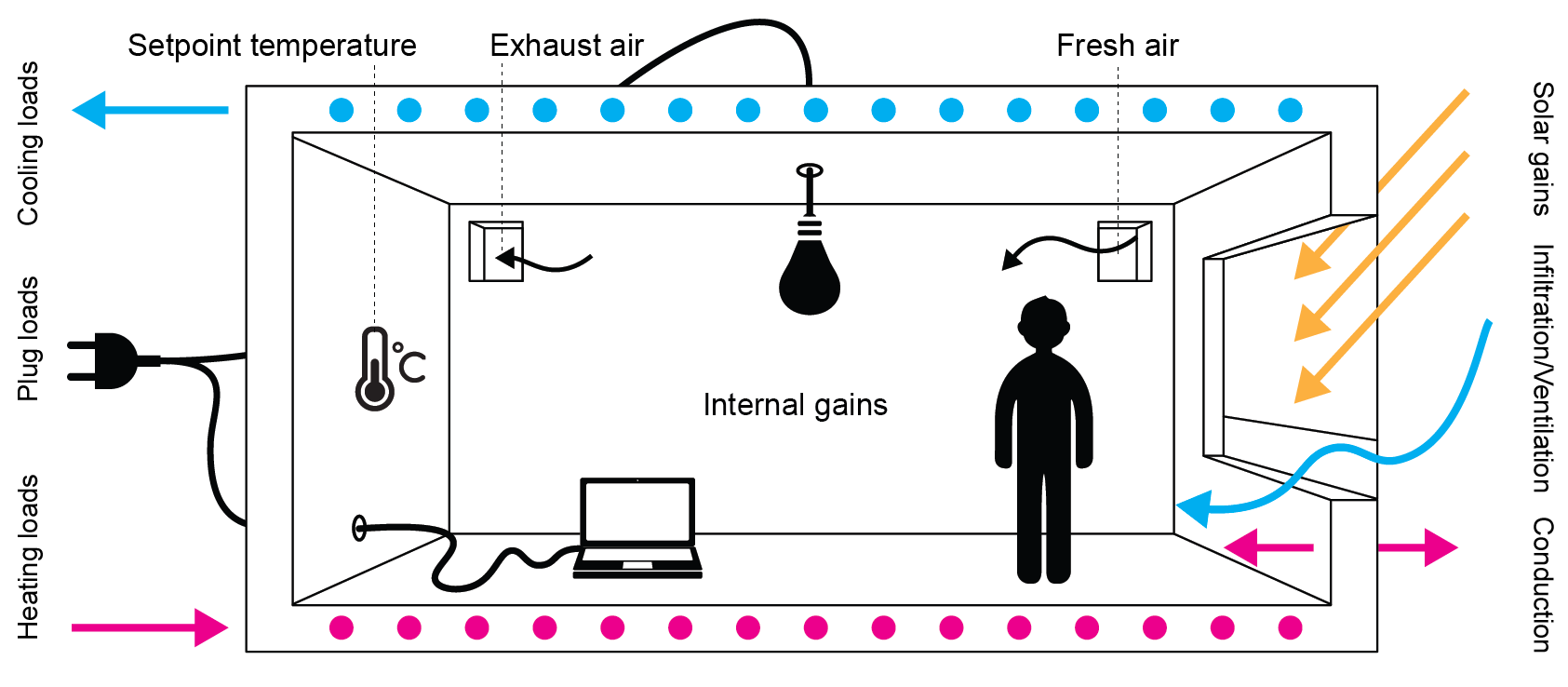
Main heat and mass transfers considered in a room
What is Archsim?
Archsim Energy Modeling is a plugin that, for the first time, brings fully featured EnergyPlus simulations to Rhino/Grasshopper and thus links the EnergyPlus simulation engine with a powerful parametric design and CAD modeling environment. Archsim allows you to create complex multi-zone energy models, simulate them and visualize results all within the Rhino/Grasshopper environment. Archsim supports advanced daylighting and shading controls, ventilation modules such as wind and stack natural ventilation, airflow-networks, simple HVAC, photovoltaics and phase changing materials. It is typically used for rapid early design exploration where building shape, window to wall ratios, facade and glazing systems and passive approaches such as shading and natural ventilation potential are tested for their impact on the building environmental performance and comfort. Simulation inputs such as model geometry, materiality, constructions and zone usage profiles are fully parametric and can be coupled with optimization algorithms within Grasshopper. Archsim is still under development and new features are added frequently. Archsim exports native IDF files that are fully customizable. Documentation, example files, community support and most importantly a copy of Archsim are available under Archsim.com. Also, follow Archsim on Facebook.
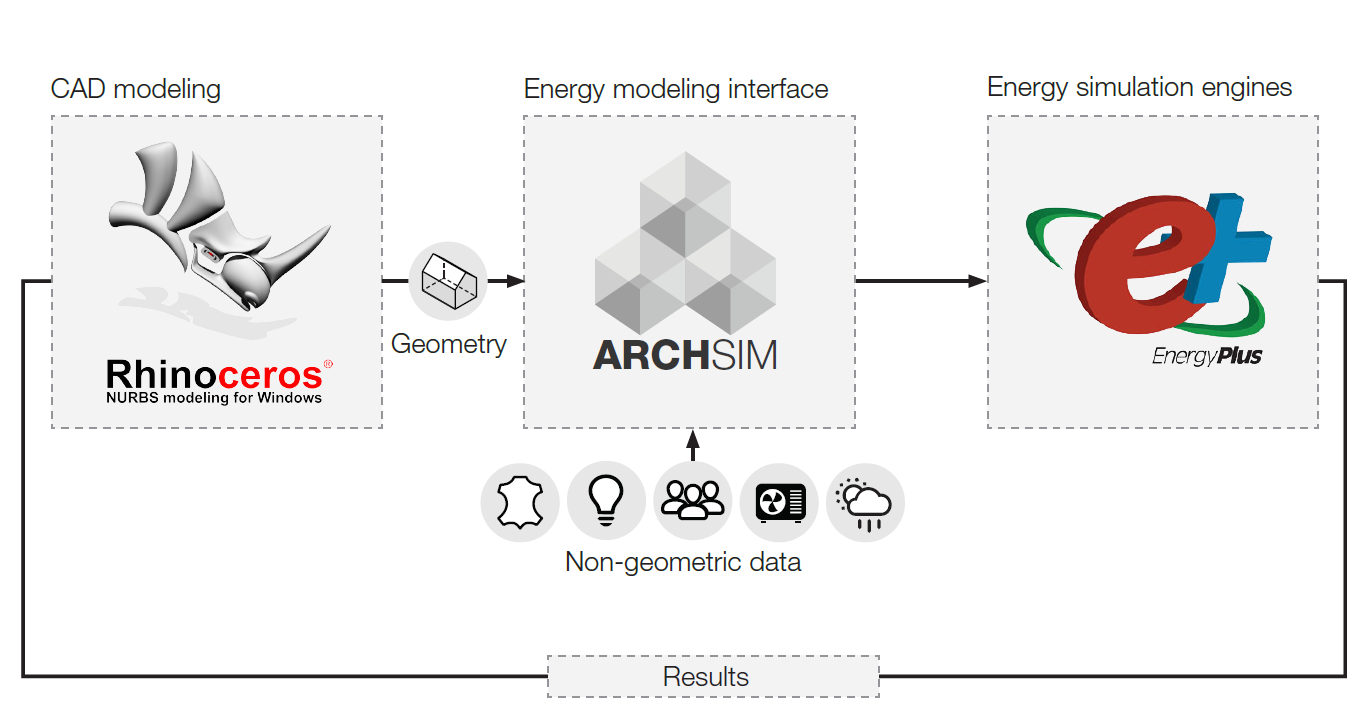 Archsim ecosystem and flow of information diagram
Archsim ecosystem and flow of information diagram